Blackjack Oak Tree Leaves
The blackjack oak (Quercus marilandica) is also known as the Jack oak, black oak, and barren oak. A small deciduous tree that grows 20 to 30 feet (maximum 90 feet) with a trunk diameter of 1 foot or less. It is similar to the post oak which also grows with blackjack oak, but the leaf lobes are more pronounced and not bristle-tipped.
Habitat: Found in upland woods of southeast Iowa
Importance of Blackjack Oak. The importance of plants lies in their great contribution to human life and the environment. The importance of Blackjack Oak is high as its benefits are more and so are Blackjack Oak Facts. Every gardener must look for the required information on this plant before planting it. Identifying trees can be trickier in the winter, but many types of oaks, such as the white oak, hold onto their leaves in the colder months—even if the leaves turn brown and die. If the oak loses its leaves, you can look for other clues, like the appearance of the bark or the shape of the buds at the ends of branches. One of the biggest threats to oak trees in Texas is oak wilt, an often deadly fungal disease which compromises the tree’s ability to retain water. Although all oaks are vulnerable to this pathogen, red oaks, including Texas oaks, Shumard oaks, blackjack oaks and water oaks are the most at risk. All oak trees may display foliage marcescence, even species that are known to fully drop leaves when the tree is mature. Seedling and young oak trees may awkwardly and irregularly hold onto leaves into winter, but with maturity, they manage to drop leaves in late fall. An example is the swamp white oak (Quercus bicolor).
Hardiness: Varies with the species of oak tree, ranging from zones 3 through 9
Growth Rate: Slow to Moderate
Mature Shape: Broad, rounded
Height: Varies with species. Often maturing between 50 to 75 feet tall. Capable of growing upwards of 100 feet.
Width:40 to 70 feet. Varies with species
Site Requirements: Best growth in moist, well-drained soils. Adaptable to adverse soil conditions.
Flowering Dates: Spring
Seed Dispersal Dates: Fall
Seed Bearing Age: 20 years
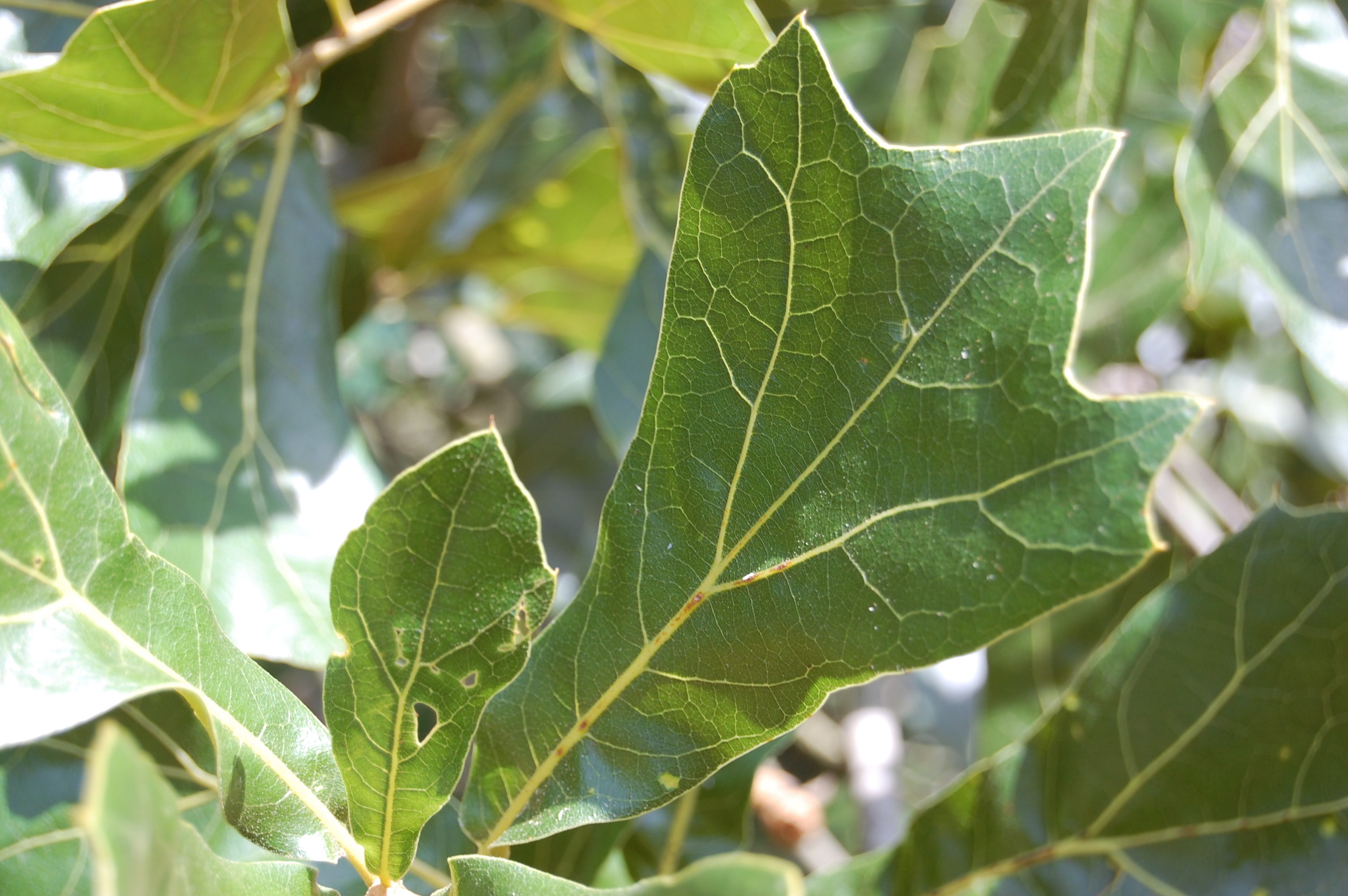


Seed Bearing Frequency: Acorns produced vary from year to year, with larger crops occurring during 'mast year,' every four to ten years.
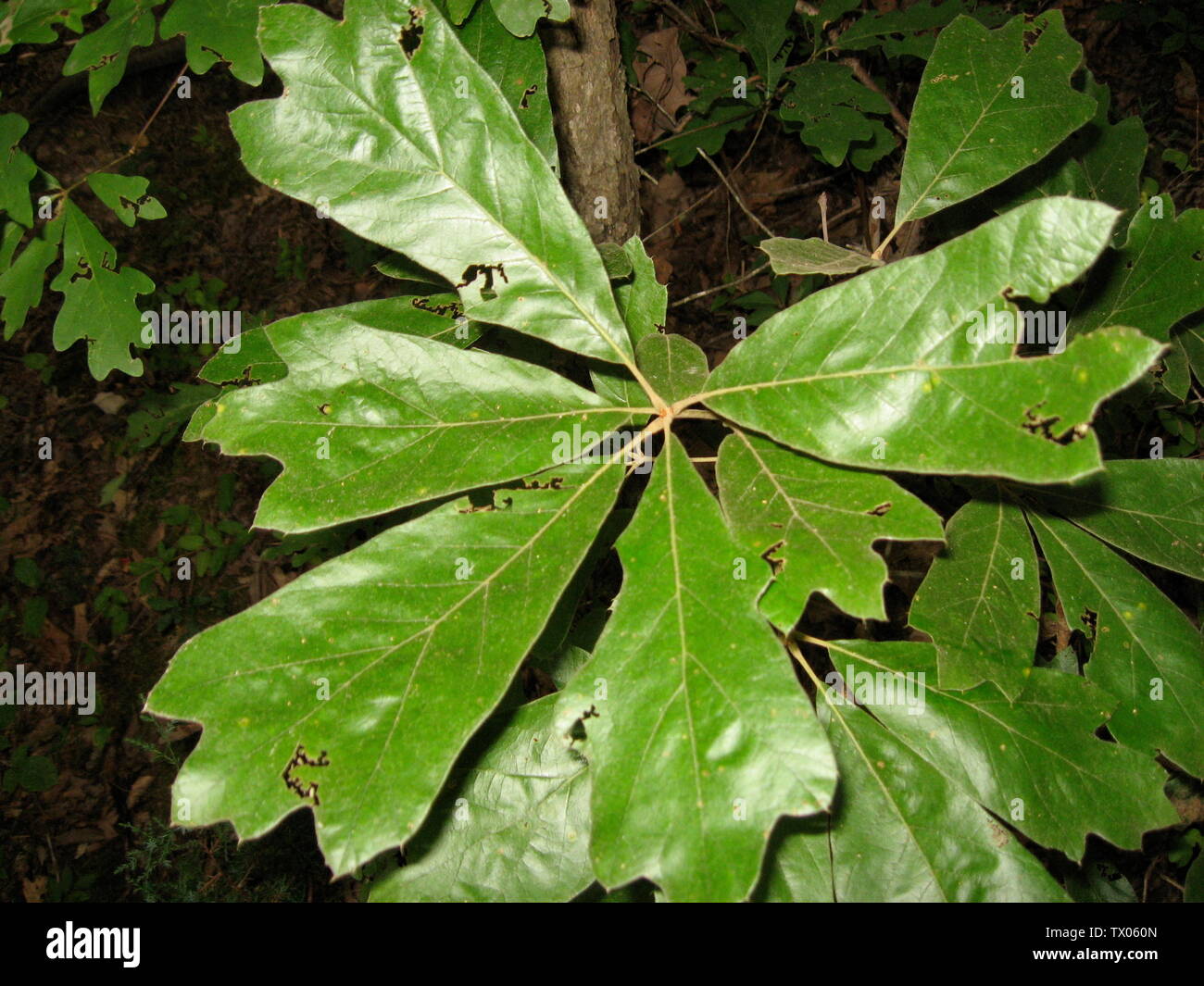
Blackjack Oak Tree Leaf Arrangement
Seed Stratification: Two to three months at 40° F or they can be set out in the fall for natural stratification and germination in the spring.
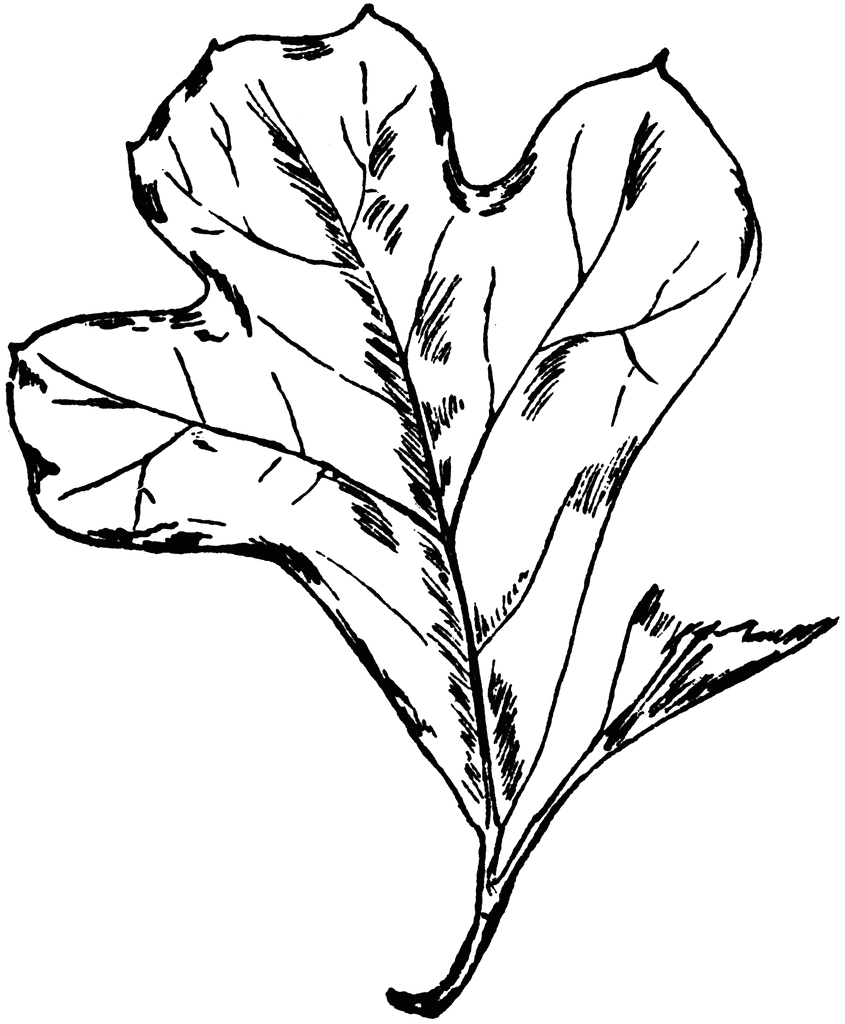
The leaves are 4 to 8 inches long, 3-lobed, bristle-tipped, taper to a rounded base, obovate in outline, thick petioles less than 1/2 inch long, top is dark yellow-green, beneath is paler with a tawny colored down.
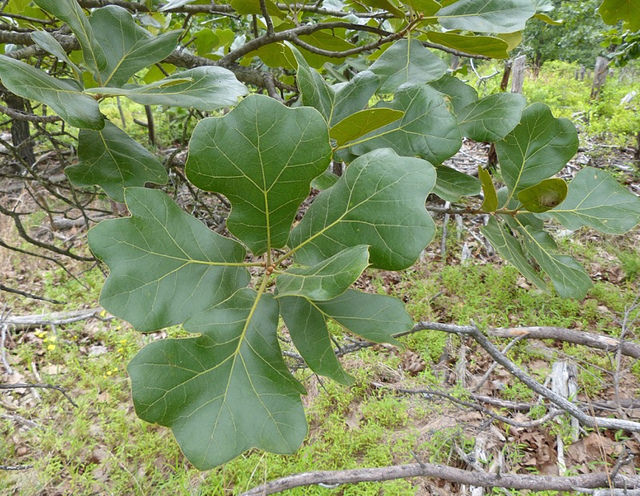

Acorns are 3/4 inch long, with a shallow cup shaped like a goblet, and somewhat hairy. The nut is ovoid shape, yellow-brown, and striated. The twigs are thick, dark red-brown and hairy, and the trunk is almost all black with deep grooves and scaly plates.

The blackjack oak is known for growing in barren, dry, sandy, or clay soils. Its range extends from southeastern New York to southern Michigan and Nebraska, south to central Florida and eastern Texas. Blackjack oak can be found in the upland woods of northeast Iowa.